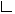 java.lang.Throwable
java.lang.Throwable
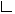 java.lang.Error
java.lang.Error
|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objectjava.lang.Throwable
java.lang.Error
public class Error
Applications should not try to catch errors since they indicate
abnormal conditions. An abnormal condition is something which should not
occur, or which should not be recovered from. This latter category
includes ThreadDeath and AssertionError.
A method is not required to declare any subclass of Error in
its throws clause which might be thrown but not caught while
executing the method.
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
Error()
Create an error without a message. |
|
Error(String s)
Create an error with a message. |
|
Error(String s,
Throwable cause)
Create an error with a message and a cause. |
|
Error(Throwable cause)
Create an error with a given cause, and a message of cause == null ? null : cause.toString(). |
|
| Method Summary |
|---|
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Throwable |
|---|
getCause, getLocalizedMessage, getMessage, initCause, printStackTrace, printStackTrace, printStackTrace, toString |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public Error()
Throwable.initCause(Throwable)public Error(String s)
s - the message stringThrowable.initCause(Throwable)
public Error(String s,
Throwable cause)
s - the message stringcause - the cause of this errorpublic Error(Throwable cause)
cause == null ? null : cause.toString().
cause - the cause of this error
|
|||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||